What is Microbiology? microbiology career
Microbiology :
microbiology is the study of microorganisms, also known as microbes. an array of diverse and generally tiny life forms, which include archaea’s, bacteria algae, fungi protozoa and viruses. The research is concerned with the nature, function and classification of these organisms as well as ways of utilizing and controlling their actions.
The disclosure in the seventeenth 100 years of living animals that were not apparent for the natural eye a significant occasion throughout the entire existence of science. This is on the grounds that starting in the thirteenth hundred years, it was thought that “imperceptible” substances were liable for the improvement of sickness and rot. The term microorganism was utilized in the last time of the nineteenth 100 years to allude to the different organic entities which were accepted to be firmly related. Microbial science developed into a science that was specific and was found, microorganisms involve a gigantic assortment of organic entities that are incredibly different.

Consistently life is inseparably intertwined with microorganisms. Close by dwelling on the external and inward surfaces of our bodies organisms flourish inside the earth, the oceans, as well as inside the air. They are plentiful, yet frequently inconspicuous microorganisms offer more than adequate proof of their reality. At times, they do so ominously, for example, when they trigger rot of materials or communicate illnesses, however frequently in a positive way, for example, when they convert sugar into wine and lager and prompt bread to rise, flavor cheeses, and make important things like insulin and anti-infection agents. Microorganisms add gigantic importance to the environment of Earth in eliminating plant and creature remains and transforming them into straightforward substances that can then be utilized in the formation of new organic entities.
microbiology, microbiologist, microbe, what are microbes, what is microbial, what is a microbial, what is a microbe, microbiologist salary, microbiologists salary, salary for a microbiologist, microbiology job, microbiology careers, salary of microbiologist,
Background information from the past
Microbial science started with the innovation of the magnifying lens. While others could have noticed organisms previously anyway they were Antoine van Leeuwenhoek Dutch draper enthusiastically for crushing focal points and making magnifying instruments that is the one to make an exact record of his perceptions. The drawings and depictions he composed included protozoans found in the creature’s guts as well as microscopic organisms that were tracked down in tooth scrapings. His documentation was great since the amplifying focal points he made were with extraordinary quality.
Leeuwenhoek shared his discoveries in a series notes to individuals from his kindred individuals at the English Illustrious Society during the last part of the 1670s. While his discoveries started a ton of interest, no one endeavored in any serious method for copying or expand the discoveries. Leeuwenhoek’s “animalcules,” as he portrayed them, stayed only a couple of peculiarities in nature to researchers of the time, and interest in concentrating on microorganisms expanded sluggish.
It was exclusively in the eighteenth 100 years, when there was a restoration of a long-running contention over the chance of life creating from nonliving matter and that the significance of microorganisms inside the structure of nature as well as in the prosperity and soundness of people became evident.

Generation spontaneous versus biological generation of life
In the early Greeks thought about that living animals could emerge in nonliving substances (abiogenesis) too as that goddess Gea might have made life from stone. Aristotle excused this conviction nonetheless, he accepted that creatures could be conceived normally from various life forms or even from soil. The impact of his thoughts on the idea of unconstrained creation was obvious as late as the seventeenth 100 years, but towards the end of the hundred years, a succession of examinations, perceptions and discussions began which in the end discredited the thought. The improvement in understanding was difficult to battle by a progression of occasions, and powers of individual will and character regularly darkening reality.
While Francesco Reid, an Italian specialist, in 1668, demonstrated that higher types of life might have begun normally, the advocates of the hypothesis pronounced that microorganisms were remarkable and might have rose this way. A few renowned names like John Needham and Lazzaro Spallanzani were enemies in this contention in the last part of the 1700s. In the start of the 1800s Franz Schulze and Theodor Schwann were the most unmistakable figures in their endeavors to expose the speculations of abiogenesis.
Louis Pasteur at long last reported the aftereffects of his definitive examination in 1864. Through a series splendid examination, Pasteur demonstrated that main existing microorganisms can bring forth the development of different organic entities (biogenesis). Present day , precise comprehension about the sorts of microscopic organisms is because of German botanist Ferdinand Cohn, whose main discoveries were distributed in 1853 somewhere in the range of 1853 and 1892. Cohn’s characterization for microorganisms, distributed in 1872, and extended in 1875, was the essential exploration of these living beings for the following couple of years.
Disease and microbes
Girolamo Fracastoro, an Italian researcher, proposed from the mid-1700s that virus was a contamination that spreads between various things. The exact idea of what occurs during transmission was not accessible for specialists for the rest of the 1800s, when the endeavors of various scientists, Pasteur preeminent among them laid out the meaning of microorganisms during the time spent maturation and infections. Robert Koch, a German specialist, fostered the technique (Koch’s hypothesizes) to demonstrate that a specific creature is liable for the particular disease.
The microbiology-based foundation was laid in the time from around 1880 until 1900. Students from Pasteur, Koch, and others discovered quickly an array of bacteria that could cause specific illnesses (pathogens). They also developed an extensive set of tools and laboratory methods to reveal the widespreadness of the microbes, their diversity, and capabilities of microbes.

The 20th century was a time of progress.
These advancements occurred during Europe. Just in the mid 1900s did microbial science gain a traction in America. A great deal of microbiologists working in America in the mid 1900s were taught with Koch and at Pasteur Establishment in Paris. After its foundation in America microbial science flourished, especially corresponding to firmly related fields as natural chemistry and hereditary qualities. In 1923, American microbiologist David Bergey laid out that science’s chief reference point, with refreshed forms of which are as yet utilized today.
Since the 1940s, microbial science seen an enormously useful time where a wide assortment of infection making microorganisms have been found and systems oversee them were made. Microorganisms likewise have been effectively utilized in enterprises Their exercises are diverted to the extent that gainful items are currently fundamental and schedule.
Microorganisms have expanded our figuring out pretty much all living organic entities. Microorganisms are easy to work with and offer a clear method for exploring the mind boggling processes that happen throughout everyday life. Subsequently, they are presently a compelling instrument to concentrate on digestion and hereditary qualities in the sub-atomic domain. This extraordinary assessment of the jobs of microorganisms has created various, and at times surprising prizes. The comprehension of the metabolic and wholesome necessities of a microorganism, as an occurrence, is many times approaches to forestalling the spread of sickness or contamination.
These advancements occurred during Europe. Just in the mid 1900s did microbial science gain a traction in America. A great deal of microbiologists working in America in the mid 1900s were taught with Koch and at Pasteur Establishment in Paris. After its foundation in America microbial science flourished, especially corresponding to firmly related fields as natural chemistry and hereditary qualities. In 1923, American microbiologist David Bergey laid out that science’s chief reference point, with refreshed forms of which are as yet utilized today.
Since the 1940s, microbial science seen an enormously useful time where a wide assortment of infection making microorganisms have been found and systems oversee them were made. Microorganisms likewise have been effectively utilized in enterprises Their exercises are diverted to the extent that gainful items are currently fundamental and schedule.
Microorganisms have expanded our figuring out pretty much all living organic entities. Microorganisms are easy to work with and offer a clear method for exploring the mind boggling processes that happen throughout everyday life. Subsequently, they are presently a compelling instrument to concentrate on digestion and hereditary qualities in the sub-atomic domain. This extraordinary assessment of the jobs of microorganisms has created various, and at times surprising prizes. The comprehension of the metabolic and wholesome necessities of a microorganism, as an occurrence, is many times approaches to forestalling the spread of sickness or contamination.
Different types of microorganisms
The major groups of microorganisms–namely bacteria, archaea, fungi (yeasts and molds), algae, protozoa, and viruses–are summarized below. Links to more in-depth reviews of each of the major groups are included.
Bacteria (eubacteria and archaea)
Microbiology developed primarily through the study of bacteria. The work conducted by Louis Pasteur in France, Robert Koch in Germany, and other researchers in the latter half of 1800s established that microbes are important for humans. According to the Historical background section, the work of these scientists proved that germ theory for illness and theories of origin of fermentation. In their labs that the techniques were developed for microscopic examination of specimens, the cultivation of (growing) bacteria in the laboratory, isolating the pure strains from mixed-culture populations and other lab manipulatives. These techniques, originally used for studying bacteria, have been modified for the study of all microorganisms–hence the transition from bacteriology to microbiology.
The organisms of the microbial community are classified as either eukaryotes, or prokaryotes and all bacteria are prokaryotic. That is, single-celled organisms that do not have an attached nucleus to the membrane. The DNA (the genetic material in the cell) is, rather than being located in the nucleus is a long, unfolded thread that has no place inside the cell.

During the 1970s, it was broadly accepted that all microorganisms are connected in advancement. This thought has been tested starting around 1977 Carl R. Hardships and co-specialists from the College of Illinois, whose concentrates on ribosomal DNA from a large number of living organic entities uncovered that two microbes created in particular ways from a typical familial structure. This prompted the improvement of another term to characterize the most unmistakable kinds of microorganisms, in particular the Eubacteria (the ordinary as well as “valid” microbes), the archaea (microscopic organisms that varied from different microscopic organisms in the previous phase of their development, and contrast from the Eubacteria) as well as the eukaryote (the eukaryotes). These are currently alluded to as the bona fide microorganisms (or they are the microbes) and contain part of the term space Microscopic organisms. The connections that developed between the individuals from the three gatherings are becoming muddled, as assessment of the DNA successions of various organisms have uncovered a heap of peculiar similitudes.
This means that the exact ancestry for today’s microbes is a challenge to establish. Many traits that are thought to be unique to distinct taxonomic classes have been observed in different microbes. For example, an anaerobic ammonia-oxidizer–the “missing link” in the global nitrogen cycle–was isolated for the first time in 1999. The bacteria (an abnormal member of the family Planctomycetes) was discovered to possess internal structures similar to the eukaryotes, a cell’s wall with Archaean traits and a type for reproduction (budding) like the yeast cells.
Microbes arrive in various shapes, like poles, circles, and twistings. The phones of an individual regularly range in size from 0.5 up to five micrometers (mm millionths of one centimeter). While they are unicellular, microbes commonly are tracked down in chains, two by two or Quadruplicates (bunches comprising of 4) or groups. Certain species have flagella, which are outer whip like designs that move the creature through fluid medium and some additionally have containers that is an outside covering for the phone. Others produce spores, a regenerative body that capabilities like seeds do in plants. One of the main trademark that microscopic organisms have is the reaction towards the Gram stain. In light of the compound and construction in the mass of cells certain microbes are gram-positive that respond to the purple shade of the stain while others are non-gram negative.
Under a magnifying lens, the archaea look like microscopic organisms, but there are huge differentiations concerning their piece of synthetics, their biochemical cycles and their surroundings. The cells of all microscopic organisms contain the synthetic fixing known as peptidoglycan. In any case, the cells of archaea come up short on synthetic substance peptidoglycan. A ton of archaea’s are known for their capacity to persevere through incredibly unforgiving conditions including outrageous degrees of salt, high temperatures or corrosive.
Extremophiles, or microorganisms live in spots such including salt pads, warm pool, remote ocean vents, and warm pools. Certain species are fit for an unmistakable compound cycle that produces methane gas by consolidating hydrogen and carbon dioxide. The methane-creating archaea dwell in conditions that are sans oxygen like marsh soil or the digestion tracts and stomachs of ruminants like sheep and steers. All in all, this arrangement of microorganisms has a wide reach in the synthetic changes they produce in their current circumstance.
Algae
Cells of microbes that are eukaryotic have a similarity to animal and plant cells in that their DNA is contained inside a nuclear membrane which is the nucleus. Microorganisms that are eukaryotic include protozoa, algae, and fungi. Collectively , protozoa and algae as well as a few fungi of lower levels are commonly known as Protists (kingdom Protista, also called Protoctista) Some are monocellular, while other multicellular.
Like microbes green growth are eukaryotes. They as plants, additionally contain the chlorophyll shade, which is green. They lead photosynthesis, and have unbending cell walls. They normally live in sodden soils and in oceanic conditions. These eukaryotes can be monocellular and minute in their size, or multicellular up to 120 meters (almost 400 feet) long. Green growth in everyday showcase a few shapes. Single-celled species could be pole formed, round or axle molded, or club-formed. Some are portable. Multicellular green growth should be visible in different shapes and levels of intricacy. They are frequently made out of fibers of cells that are joined from one finish to another. In specific species, these fibers join into plant-like, naturally visible bodies. Green growth are additionally tracked down in states. Some are just totals of single cells, while others have different cell types that have particular purposes.

Fungi
Parasites are eukaryotic species that are like green growth. They have inflexible cell walls and are either multicellular or unicellular. Some are little in size, while others are a lot bigger in structure like section parasites and mushrooms that foster in clammy soil or on logs. Rather than green growth, parasites can need chlorophyll, and that implies they can’t perform photosynthesis.
They don’t ingest food, however they should retain the disintegrated supplements of the general climate. Of the organisms that are named microorganisms, those which have multicellular designs and produce filamentous minuscule designs are normally called molds. Then again, yeasts are organisms that are unicellular.
In molds , cells are tube shaped in structure and are joined start to finish to frame string like fibers (hyphae) which can bear spores. Collectively, hyphae can be tiny in aspects. Notwithstanding, when huge amounts of hyphae assemble for example or on a slice of bread , or on a piece of natural product jam, they make a fluffy mass known as mycelium, which is evident to an independent eye. v
The yeasts that are unicellular arrived in various assortments, going from round egg-formed, to filamentous. They are known for their capacity to change over starches, bringing about carbon dioxide and liquor in refreshments like wine and bread.
Protozoa
Protozoa or protozoans are single-celled microorganisms that are eukaryotic. Protozoa can be oval or spherical. Others are extended. Others have distinct forms at various stages of their life. They can grow as tiny as 1 millimeter in size and as big as 2,000 mm or 2 millimeters (visible in the absence of magnification). Similar to animal cells, protozoa have no wall cells, but are capable of moving at some phase of their life and also ingest food particles; however the protozoa of phytoflagellates are akin to plants, and obtain the energy they require through photosynthesis. Protozoan cells are characterized by the internal cells of an animal. Certain cells can swim through the water with the beat of their hair-like appendages (cilia) and flagella. Their swift, darting motion in a pond drop water is apparent when looking under the microscope.
One-celled critters (likewise amoebae) are not swimmers but rather can slither across surfaces by broadening part of themselves in pseudopods, and after that permitting the rest the cell to move through the expansion. This sort of movement is alluded to as amoeboid movement. These protozoans (phylum Apicomplexan) are so named since they structure lethargic bodies, alluded to as spores, over the span of their lives. Protozoa are tracked down in different conditions and are especially pervasive in oceanic conditions.
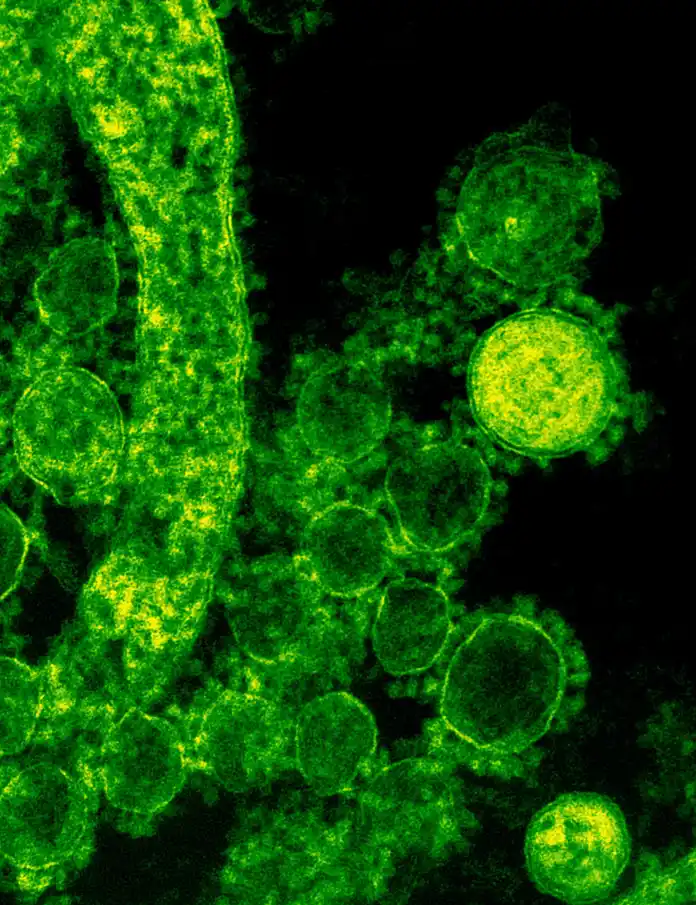
Viruses
Viruses, which are considered to be to be living things, part of the field of microbiology. They come in a variety of forms, and are widespread in the natural world that infect plants, animal cells and microorganisms. The subject area where they are examined is known as the field of virology. All viruses are considered to be obligate parasites, that is to say they don’t have the metabolic machinery that they can use to generate the energy needed to generate proteins or create it and proteins, which is why they rely on cells of the host to perform the essential tasks.
Once inside a cell viruses possess genes that take over the cells’ energy-generating and protein-synthesizing mechanisms. Apart from their intracellular forms they also possess an extracellular version that transports the nucleic acid of the virus between host cells and the next. In this type of infectious form viruses consist of an nucleic acid , which is surrounded by a protective protein coat known as the capsid. The capsid shields genes that reside outside of the host cell. It is also a vehicle to allow entry into a host cell since it binds to receptors on the cell’s surface. The mature and structurally stable viral particle is known as virion.
The electron microscope is possible to identify the morphological features of viruses. They typically range in size between 20 and 300 nanometers (nm billionths of centimeter). Because the majority of viruses are smaller than 150 nanometers and are therefore over the resolution limit of the microscope light and are only visible with electron microscopy. Utilizing materials of known dimensions for comparison macroscopics can identify the size and shape of individual virions.
Prions
In contrast with infections Prions (articulated “pree-ons”) are the most essential of microbes that cause sickness. Like infections, they are parasites, however they can’t create none of the hereditary materials. While prions are self-imitating proteins, they have been connected to the reason for different sicknesses, for example, ox-like spongiform and encephalopathy (frantic cow illness) and may assume a significant part in the improvement of various different sicknesses.
Lichens
Lichens are a sort of beneficial interaction. A collaboration between two distinct life forms each increases. Lichens are comprised of the photosynthesis microorganism (an alga or Cyanobacterium) that is filling in cozy relationship with a mushroom. A normal lichen contains the top layer of a tight-woven mycelium of parasitic life and a center layer wherein the microorganism that is photosynthetic lives in, and a lower mycelium layer. Through this mutualistic relationship photosynthesis, the microorganisms that produce photosynthetic substances make nourishment for the growth and thusly, the organism fills in as a defensive layer to green growth and Cyanobacteria. Lichens assume a vital environmental part, and in addition to other things, they are fit for changing stone into soil.
Slime molds
The sludge molds represent a natural and ordered puzzle as they’re neither typical protozoa or growths. At the point when they are in one of their formative stages they look like protozoa since they don’t have cell walls, have amoeboid developments, and furthermore ingest particles of supplements. At the hour of their proliferation, they foster fruiting bodies and sporangia which are walls-like spores like the typical parasites. The ooze molds are delegated parasites. There are two sorts of ooze molds, to be specific the sludge molds with cells and the ooze molds with acellular design.
Study of microorganisms
Like many disciplines research, the investigation of microorganisms can be ordered into two summed up , and in some cases overlaid classes. As opposed to essential microbial science, which tends to issues concerning the science of microorganisms applied microbial science is the utilization of microorganisms to accomplish explicit objectives.
Basic microbiology
The study of microorganisms’ biological processes requires the use of various procedures and specific equipment. The characteristics of microorganisms’ biology are summarized in one of the categories: Morphology nutrition as well as physiology, reproduction, growth metabolism, pathogenesis antigenicity, as well as genetic characteristics.
Morphology
Morphology is the term used to portray the size, shape or plan of the cells. The assessment of the microbial cell requires the utilization magnifying lens, yet too the readiness of cells in a manner that is reasonable for the particular sort of magnifying instrument. In the early years into the last part of twentieth century it was the compound magnifying lens that turned into the most well-known instrument utilized in microbial science. Light magnifying lens as a rule have an amplification of 1000x and a most extreme amplification of around 2000 x. It is feasible to notice examples subsequent to being stained with one of the numerous techniques to uncover specific morphological elements or in live perfect examples in “wet mount. “wet mount.”

microbiology, microbiologist, microbe, what are microbes, what is microbial, what is a microbial, what is a microbe, microbiologist salary, microbiologists salary, salary for a microbiologist, microbiology job, microbiology careers, salary of microbiologist,
microbiology,microbiology lecture,microbiology (field of study),introduction to microbiology,general microbiology,concepts of microbiology,microbiology job,kmu microbiology,microbiology mcq,microbiology mcqs,basic microbiology,microbiology usmle,mcq on microbiology,bsn microbiology#,applied microbiology,scope of microbiology,career in microbiology,microbiology lectures,microbiology af somali,basics in microbiology,microbiology freshers
microbiology,microbiology jobs,career in microbiology,bsc microbiology jobs,msc in microbiology,microbiology career,msc microbiology jobs,bsc in microbiology,jobs in microbiology,microbiology career jobs and salary,bsc microbiology,microbiology job opportunities,#microbiology,government jobs in microbiology,microbiology jobs salary,microbiology salary,private jobs in microbiology,microbiology job,microbiology career option,bs microbiology
cheapest car insurance, comprehensive car insurance, best car insurance for you, vehicle insurance, policybazaar car insurance, third party insurance, car insurance price, car insurance scams, car insurance rates.











